CONTINUOUS GLUCOSE MONITORING (CGM)
 Continuous glucose monitoring (CGM), is a major technical advancement, contributing to our understanding of the individual’s blood glucose profile. This is a wearable biosensor device that is placed on the skin with a tiny filament attached to it inserted in to the skin. It provides real-time blood glucose levels that is measured in the interstitial fluid and can provide valuable data about blood glucose profile. This information is vital to people with Type 1 or Type 2 diabetes, for whom high blood sugar levels (hyperglycemia) or low blood sugar levels (hypoglycemia) can be life-threatening. CGM devices are also valuable for people with borderline diabetes, or without metabolic impairment, serving as a window onto how diet and lifestyle decisions affect their health. Consistently high glucose levels or frequent glucose spikes and crashes can lead to short-term health effects like fatigue, brain fog, depression and may be associated with several chronic diseases, including cancer, cognitive decline, stroke, and cardiovascular disease. It can help individuals maintain stable glucose levels before metabolic dysfunction like insulin resistance and prediabetes is initiated and sets the stage for more severe disease.
Continuous glucose monitoring (CGM), is a major technical advancement, contributing to our understanding of the individual’s blood glucose profile. This is a wearable biosensor device that is placed on the skin with a tiny filament attached to it inserted in to the skin. It provides real-time blood glucose levels that is measured in the interstitial fluid and can provide valuable data about blood glucose profile. This information is vital to people with Type 1 or Type 2 diabetes, for whom high blood sugar levels (hyperglycemia) or low blood sugar levels (hypoglycemia) can be life-threatening. CGM devices are also valuable for people with borderline diabetes, or without metabolic impairment, serving as a window onto how diet and lifestyle decisions affect their health. Consistently high glucose levels or frequent glucose spikes and crashes can lead to short-term health effects like fatigue, brain fog, depression and may be associated with several chronic diseases, including cancer, cognitive decline, stroke, and cardiovascular disease. It can help individuals maintain stable glucose levels before metabolic dysfunction like insulin resistance and prediabetes is initiated and sets the stage for more severe disease.
WHAT IS A CONTINUOUS GLUCOSE MONITOR?
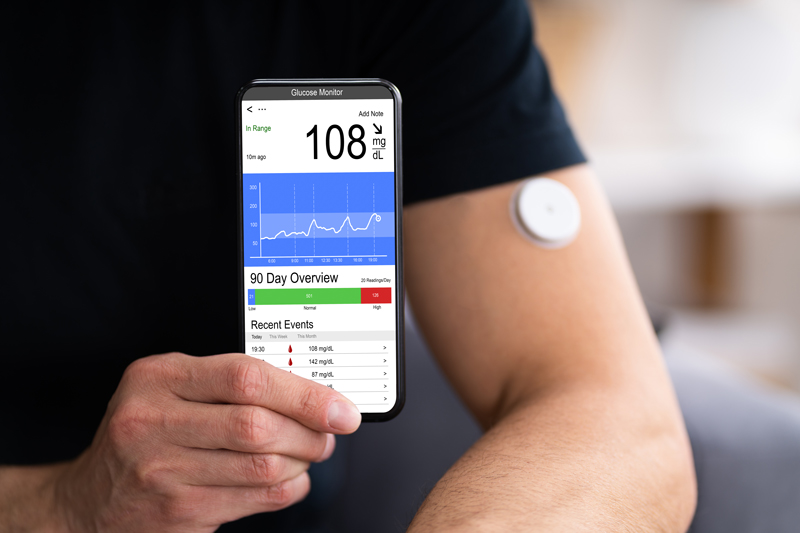 A continuous glucose monitor is a plastic disc (thicker than a quarter) that sticks to the skin by a tiny filament, typically on the upper arm or the stomach. It sends glucose data continuously (at least every 5 minutes) to a smartphone or handheld reader device, where the user can view it on a graph or chart. People who use insulin pumps for Type 1 or type 2 insulin requiring diabetes may have their CGM connected to an insulin pump that can automatically deliver insulin if their blood sugar gets too high. Most CGMs last anywhere from 10-15 days (depending on the brand) before they need to be replaced. The filament incorporated in the device is coated with an enzyme called glucose oxidase, which converts glucose to hydrogen peroxide. The hydrogen peroxide reacts with platinum to break down into hydrogen, oxygen, and electrons, which generate current. The device wirelessly transmits this signal to a handheld reader or smartphone, which uses an algorithm to convert the electrical signal to a glucose reading.
A continuous glucose monitor is a plastic disc (thicker than a quarter) that sticks to the skin by a tiny filament, typically on the upper arm or the stomach. It sends glucose data continuously (at least every 5 minutes) to a smartphone or handheld reader device, where the user can view it on a graph or chart. People who use insulin pumps for Type 1 or type 2 insulin requiring diabetes may have their CGM connected to an insulin pump that can automatically deliver insulin if their blood sugar gets too high. Most CGMs last anywhere from 10-15 days (depending on the brand) before they need to be replaced. The filament incorporated in the device is coated with an enzyme called glucose oxidase, which converts glucose to hydrogen peroxide. The hydrogen peroxide reacts with platinum to break down into hydrogen, oxygen, and electrons, which generate current. The device wirelessly transmits this signal to a handheld reader or smartphone, which uses an algorithm to convert the electrical signal to a glucose reading.
There are three primary manufacturers of CGMs in the US: Abbott, makes the Freestyle Libre monitor (the latest version is 3 Plus that last for 15 days and measures glucose every minute and updates glucose values in the app every 5 minutes); Dexcom makes the Dexcom (latest version G7, that last for 10 days) ; and Medtronic makes the Guardian system(last 7 days) that is designed to works with the Medtronic pump. These CGM systems provide real-time blood glucose reading compared to blood glucose levels measured by glucometer or laboratory fasting plasma glucose that provides only a single measurement which is a snapshot in time. These single measurements fail to reveal the fluctuations in the blood sugar spikes or crashing (glycemic variability). They also fail to show glucose trends over time or the effect of variety of foods. Continuous glucose monitoring is like listening to the orchestra rather than just individual notes.
CGMS ALSO PROVIDE THE FOLLOWING INFORMATION THAT CAN BENEFIT PEOPLE WITH OR WITHOUT DIABETES:
- Glycemic variability: Ideally, blood glucose should remain stable and only slightly rise after meals. High glycemic variability, means blood glucose is frequently “spiking and crashing”. Significant glucose variability leads to diabetes, metabolic dysfunction, insulin resistance, heart disease, etc. This is an indication that insulin production is not sufficient to control blood glucose.
- Reaction to foods: Blood glucose response to foods is variable in different individuals. It also depends on overall health, fitness, previous food consumption, microbiome, sleep quality, stress and genes. Considering these factors, CGM data provides a detailed view of overall metabolic health as it relates to blood glucose level.
- Optimizing metabolism: Our primary sources of fuel are glucose and fat. Burning fat produces ketones. Insulin is produced when our blood glucose is high and this blocks fat burning. Using a CGM will assist in choosing the right foods to stabilize blood glucose. Our body can be trained to switch to fat burning spontaneously.
- Recognize early metabolic dysfunction: It is well known that insulin resistance may develop up to ten years or more prior to elevation of fasting blood glucose level. CGM can help us evaluate the post meal blood glucose response to foods, giving us insight into how our body handles a glucose load. Therefore, the earlier we catch metabolic impairment, the easier it is to initiate measures to prevent prediabetes or diabetes.
- Off label use of CGM: Healthcare professionals are increasingly prescribing CGMs to people without diabetes to help provide feedback to optimize health. Recently certain CGM brands have made over the counter versions of their products with varying capabilities.
CONCLUSION
Continuous glucose monitoring can improve the quality of life, whether the individual has diabetes or not. Access to consistent and accurate data about blood glucose can help individuals make healthy diet and lifestyle choices to support longevity and wellbeing.
This writing is for information only and should not be considered a medical advice.